Designed for high volume parts processing
(1) Aluminum alloy die casting: light weight, high heat dissipation, strong structure
Aluminum alloy die casting adopts cold chamber machine forming, which is suitable for high flow materials such as ADC10/ADC12. It can quickly fill and shape complex ribs in a thin wall of 0.9 mm, greatly reducing the weight of parts (ρ≈2.7 g cm⁻³) and maintaining excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
✅The thermal conductivity of aluminum itself is as high as 150 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹, which is the first choice for heat sinks, automotive and motorcycle electronic control housings and lightweight structural parts;
✅The mold working temperature is 180–220 °C and the injection pressure can reach 2 000 bar, which is enough to fully replicate the details;
✅The single-piece cycle is about 30–60 seconds. After forming, CNC finishing, sandblasting, anodizing or liquid/powder baking can be performed, which can enhance corrosion resistance and present a colorful appearance.
If you care about reducing weight, heat dissipation and medium-thick wall structural rigidity, aluminum alloy die casting is the best solution for both performance and cost efficiency.
Aluminum extrusion is a versatile manufacturing technology that can press aluminum alloy materials into metal extrusion dies with consistent cross-sectional shapes. Large stamping machines can push heated aluminum billets through the die through extruders or hydraulic presses and out of the die holes. Aluminum extrusion is suitable for making metal frames, housings, radiators, automotive parts, bicycle frames, etc., suitable for large to small batch production.
(2) Zinc alloy die casting: high precision, fast pace, perfect electroplating
Zinc alloy (Zamak #3/#5, etc.) is hot-chamber die-casting. The integrated furnace pool allows the piston to directly take the soup, and a mold cycle can be completed in 15-20 seconds;
✅The low melting point (≈420 °C) makes the mold life easily exceed one million molds, while allowing 0.6 mm or even thinner wall thickness and IT12-IT13 level dimensional accuracy, which is particularly suitable for micro gears, 3C appearance parts and mechanism fasteners.
✅Zinc has low fluidity and solidification shrinkage (≈0.6%), and the surface of the casting is naturally dense, with Ra up to 0.8 µm. It can be directly electroplated with bright nickel, chromium or trivalent chromium, presenting a mirror or matte metal texture;
✅Secondary processing can also be easily CNC, spray-painted or silk-screened
The high density of zinc alloy (ρ≈6.6 g cm⁻³) makes zinc alloy more advantageous in situations where counterweight, wear resistance or high toughness are required. If your product pursues the ultimate appearance, thin-wall precision and ultra-high-speed mass production, zinc alloy die-casting will bring you the best solution with both manufacturing cost and aesthetics.
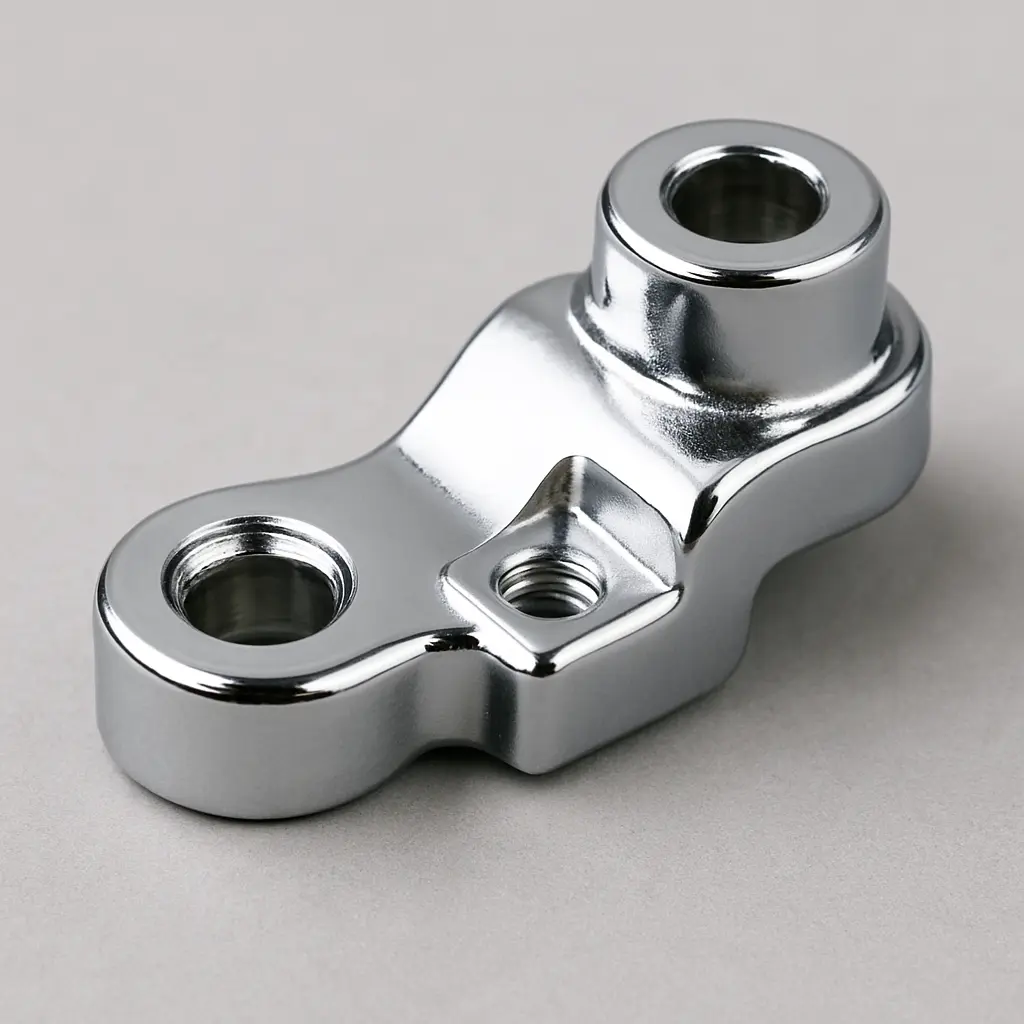


The professional team at IDMockup tailors production processes to meet each client’s specific needs, ensuring that parts not only meet the required specifications but also fulfill quantity and delivery schedule expectations.
| Aluminum alloy die casting | Zinc alloy die casting | |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Type | Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine | Hot chamber die casting machine Aluminum has a high melting point (≈ 660 °C) which will corrode the hot chamber nozzle, while Zinc has a low melting point (≈ 420 °C) which can be directly immersed in the tin bath to quickly cast the material. |
| Melt feeding | External furnace → Scoop → Inject into pressure chamber | Furnace and pool integrated, piston directly absorbs (aluminum must consider the oxidation scale; zinc does not need to consider) |
| Sample cycle (typical) | 30 ~ 60 seconds/item | 15 ~ 20 seconds/item (Low melting point + short piston stroke in hot chamber, the circulation rate of zinc parts can be 1.5 to 2 times faster than that of aluminum) |
| Mold life | About 100k shots | > 1 M shot (low zinc pouring temperature, less abrasion, slow fatigue of steel mold) |
| Minimum wall thickness | 0.9 mm | 0.6 mm (Zinc has good fluidity and small solidification shrinkage, and can be used to make ultra-thin precision parts) |
| Dimensional accuracy | IT13 ~ IT14 | IT12 ~ IT13 |
| Density/weight | 2.7 g cm⁻³ → Lightweight | 6.6 g cm⁻³ → Heavier (suitable for counterweights and structural strength parts) |
| Strength-to-weight ratio | Excellent | Medium |
| Thermal conductivity/heat dissipation | High (≈ 150 ~ 180 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹) (preferred for heat sink) | Medium (≈ 110 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹) |
| Surface brightness | Ra 1.0 ~ 2.0 µm (sandblasting/polishing required) | Ra 0.8 µm can be directly electroplated (the zinc casting surface is dense, suitable for bright nickel and chromium) |
| Secondary Processing | CNC, anode, powder, liquid paint, de-flash | After CNC and deburring, it can be directly electroplated, painted, de-flashed, and de-watered |
| Relative cost (same quantity) | Expensive molds and low material cost per piece | The mold is cheap, and the cost of a single piece of material is slightly higher (the hot chamber mold has a simplified structure and a long life) |
| Injection speed | 30 ~ 70 ms⁻¹, high pressure 1500 ~ 2000 bar (aluminum requires higher pressure to fill thin walls) | 15 ~ 30 ms⁻¹, medium pressure 700 ~ 1000 bar |
| Solidification shrinkage | 1.2% (ADC10) → Porosity control is relatively difficult (although aluminum parts can be colored by anodizing, the risk of pinholes is high, so chemical nickel plating/spraying is often used to seal the pores.) | 0.6% → Fewer pores (zinc parts can be made into airtight parts without secondary impregnation) |
| Mold temperature | 180 ~ 220 °C | 140 ~ 160 °C (low zinc mold temperature, low risk of thermal cracking/thermal fatigue) |
| Typical Alloy | ADC1, ADC3, ADC6, ADC10 … (JIS AD) | ZAMAK #3/#5, ZA-8, Mazak, EZAC |
| Common Applications | Electronic/automotive, heat sinks, automotive structural parts | 3C appearance parts, buckles, gears, precision shaft seats, chrome-plated buttons, connector terminal shells |
Die Casting – Scope of Services
Produce batch entities based on the requirements, quantity, drawings and other relevant information provided by customers
Make molds for mass production and produce according to ISO standards
According to the processing drawings or customer samples, the product is post-processed by CNC machine/EDM, and modified to the appearance required by the customer through electroplating or anodizing and other appearance post-processing processes.

We provide just-in-time production based on customer needs, minimizing storage and inventory costs. This approach ensures efficient production while reducing overhead related to warehousing and excess stock.
Basic Casting Materials
Metals
Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, easy to machine, and corrosion-resistant, making it commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries for lightweight components.
Common material choices:
◆ ADC1, ADC3, ADC6, ADC10 … (JIS AD)

Zinc has excellent corrosion resistance, good fluidity, and is easy to machine with CNC. It is often alloyed with other metals for processing and casting.
Common material choices:
◆ ZAMAK #3/#5, ZA-8, Mazak, EZAC
CMF Options

We provide a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.

We offer superior surface finishes that enhance part durability and aesthetics for applications requiring smooth or textured surfaces.
Applied Industries
IDMockup offers top-notch manufacturing capabilities, whether for rapid prototyping or custom production orders. Our self-owned factories and satellite factories are equipped to efficiently produce complex, high-quality parts.
👉 For more about our latest news, technology and equipment, please follow our official Facebook, X (Twitter) and official blog!